In recent years, with the continuous investment of mobile phone manufacturers, the smart watch market is full of vitality. In the first half of 2021, the global shipment of smart watches exceeded 86mu, with a year-on-year increase of 32%. With the peak season of the consumer market in the second half of the year, the annual shipment is expected to exceed 200mu. In the post epidemic era of covid-19 raging around the world, smart watches have been given a new mission, integrating functions that can reflect people's exercise status and health indicators such as blood oxygen, heart rate, ECG monitoring, body temperature, blood glucose and blood pressure monitoring. Under the new normal of focusing on sports health, how does Ti core technology help and lead the new trend of smart watches?
Generally, a smart watch with both sports and health management functions is composed of several functional modules shown in Figure 1. Today, we will mainly introduce ti's solutions for the two most concerned functional modules of battery charging management and body temperature monitoring, in order to help engineers provide optimal device selection and reference design guidelines during project development.
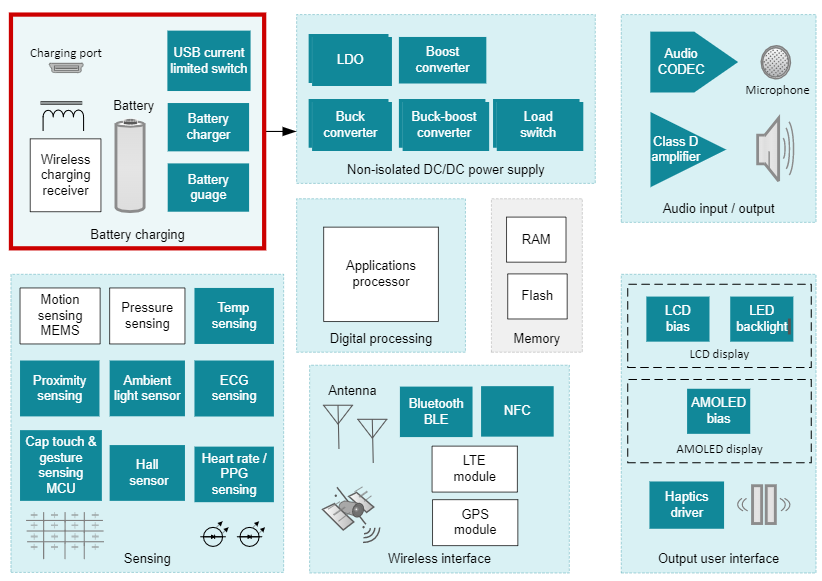
Figure 1 Smart watch system block diagram
1. Battery charging management
Bq25170: linear charging IC, supporting various charging voltages of 1V, 4.2V, 4.35v and 4.4V, 30V maximum input withstand voltage, 800mA charging current, ultra-low 0.5ua battery leakage current, 2 * 2qfn ultra-small package
Core highlights: the resistance configuration is simple and easy to use, and the high-voltage lithium battery has a long life
Typical application circuit:
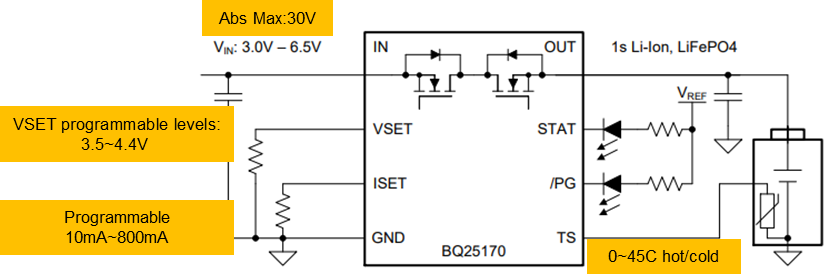
Figure 2 Bq25170 typical application circuit
The overall solution is only 9 mm ^ 2 (8 pin). Refer to figure 3 for PCB layout
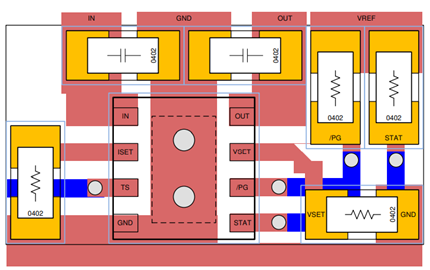
Figure 3 Bq25170 layout example
Bq25180: linear charger, supporting 5 ~ 4.65v various charging voltages, 25V maximum input withstand voltage, 1A charging current, ultra-low 10na shipping mode, only 3ua battery leakage current, powerpath & JEITA function, 1.6 * 1.1mm WCSP ultra-small package
Core highlights: I2C is flexibly configured, with path management, shipping mode and temperature regulation
Typical application circuit:
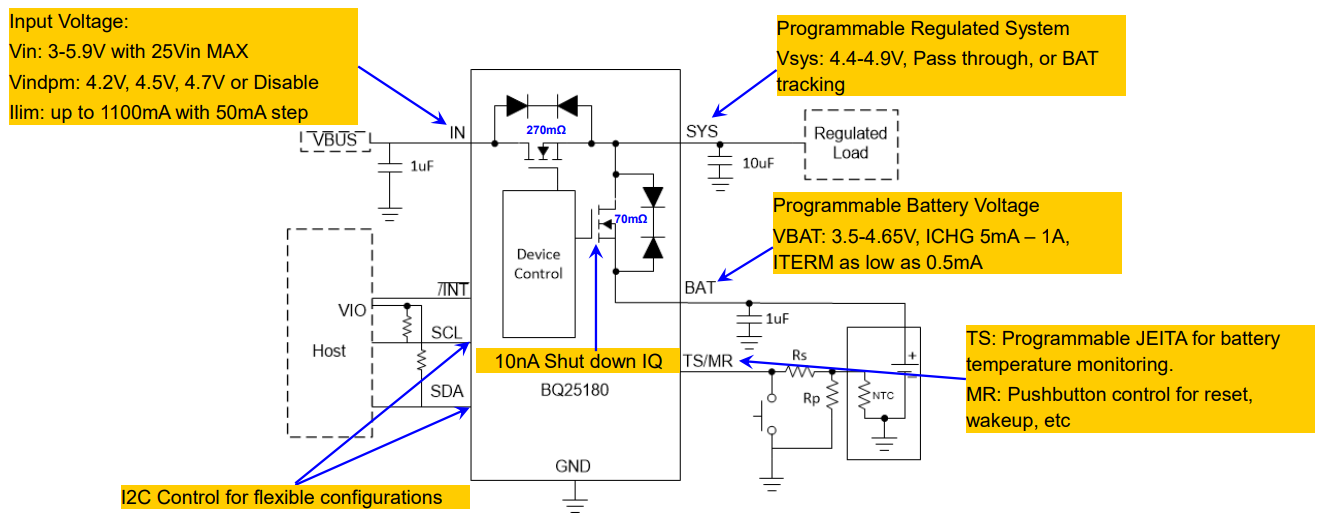
Figure 4 Bq25180 typical application circuit
At the same time, bq25180 also has the JEITA function of similar products in the leading market, meets the temperature control requirements of terminal products in the charging process, and will bring more safe and reliable experience and guarantee to users.
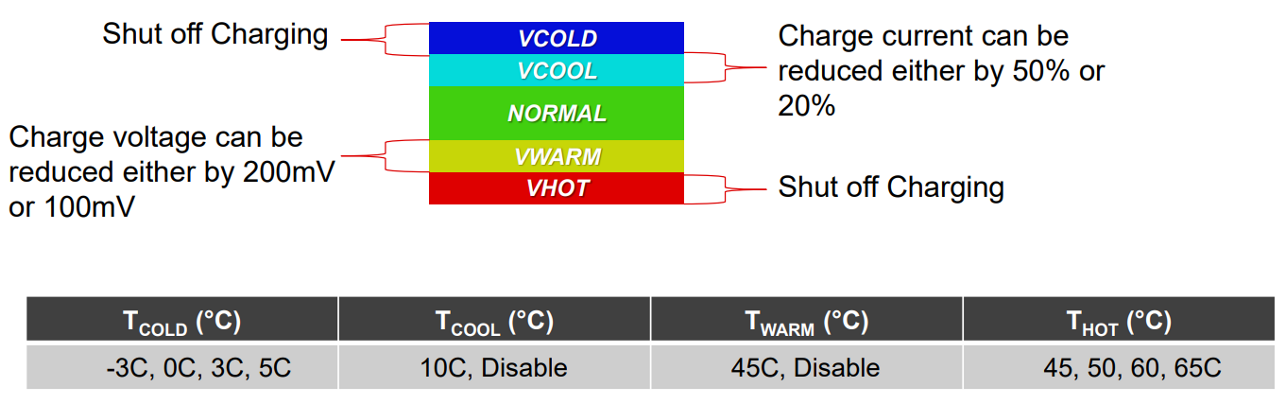
Figure 5 Adjustable JEITA: -3 ~ 65℃
Bq25618 / 9: switch charger, 5A charging current, powerpath, integrated 1A boost output, ultra-low 9ua battery leakage current, powerpath & JEITA, 2.0 * 2.4mm WCSP & 4 * 4mm QFN ultra small package
Core highlights: I2C configuration, 1.5A efficient fast charging, integrated boost boost output
Typical application circuit:
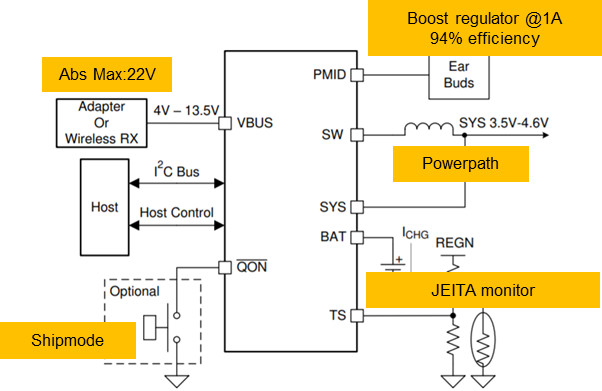
Figure 6 Bq25618 typical application circuit
2. Temperature monitoring
Smart watches with temperature monitoring function have been mentioned as early as a few years ago, but they have not attracted market attention. With covid-19 sweeping the world, this function has attracted more and more attention from consumers. Ti has worked in this field for many years, and its product catalog covers a variety of applications. Tmp117, which is mainly promoted in the intelligent wearable market, has a temperature detection accuracy of 0.1 ℃.
Tmp117: up to 16bit data conversion accuracy, + / - 0.1 ℃ (- 20oC to 50oc) medical temperature detection accuracy, digital output, built-in EEPROM without additional correction, I2C temperature early warning, 3 5uA@1Hz Current consumption, 2 * 2wson, 1 * 1.6wcsp ultra small package
Core highlights: ultra-high precision automatic calibration, ultra-low power consumption and ultra-small package
Typical application circuit:
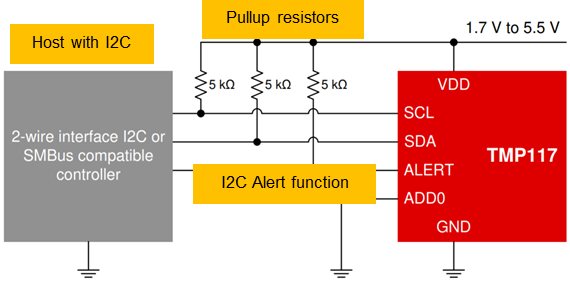
Figure 7 Tmp117 typical application circuit
In temperature monitoring, the biggest design challenge is how to fully transmit the temperature of the skin surface to the sensor as much as possible to ensure the reliability of the detection results. Ti models and analyzes the heat conduction path under the wrist of the human body, and provides a number of application design guidelines for engineers' reference, such as layout design guidelines and FPC board reference design, which can accelerate the design process and easily solve the problem of inaccurate temperature detection caused by mechanical structure.
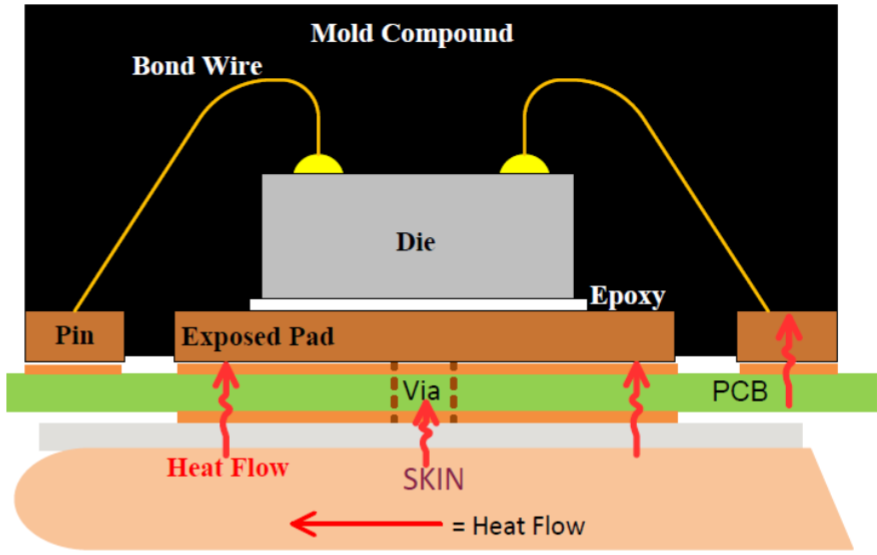
Figure 8 Heat conduction path (skin)